Developing a product is undoubtedly one of the most brainstorming and comprehensive processes. But being comprehensive doesn’t mean that every product will be eventually successful. From curating a strong idea to transforming it into a viable product and releasing it, it is a comprehensive process. The journey of an idea to market release and after maintenance, the life cycle of a product is not only comprehensive but also complex.
The process of developing a product keeps shifting and changing as per the demands of the market and the customers. Thus, developers and business owners need to be informed about the whole process of developing a product from ideation to releasing it and beyond. The process of product development doesn’t end on its release. It asks for regular monitoring and improvements to make sure that your product is always relatable for your customers.
According to a report from Market Research Future, the Product Life Cycle Management Market size is projected to grow from USD 48.14 Billion in 2024 to USD 78.33 Billion by 2032, exhibiting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.27% during the forecast period (2024 – 2032). Additionally, the product life cycle management Market Size was valued at USD 44.91 Billion in 2023.
Make sure that you get success in the very first attempt at developing a product as we will go through the comprehensive guide to understand what is Product Development Life Cycle in this blog.
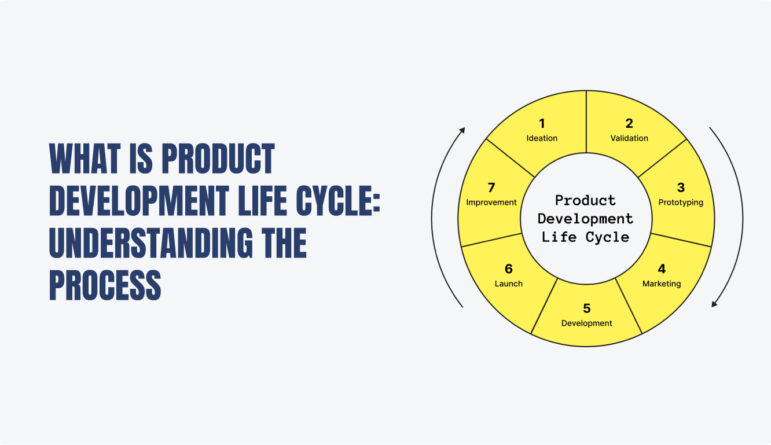
As the term describes itself, it is the whole life of a product- from ideation to its release to the market and after release and required maintenance. The process of the Product Development Life Cycle (PDLC) describes all the steps teams have to follow in order to develop a product and make it available to the public in-depth. The process includes identifying what is the market demanding, conceptualizing the product, creating a product roadmap, releasing the product, collecting feedback, and keeping up with the maintenance on the basis of the collected feedback.
Developing a product that has a strong demand in the market and that can provide customers with a new solution is a comprehensive brainstorming process. Following are some of the
This is the process in which ideas are explored. A product solves a specific problem of the customers. This is the stage where the team evaluates where the audience is might be seeking the solution in their life. Coming up with a number of ideas is the motive of this stage. The possible ideas related to the product are curated on the basis of customer needs, market research, and new technological trends.
Following are some of the things to consider in your 1st step that will help you curate a product idea that is unique:
This process is used to validate all the data found in the initial research. The findings are validated by conducting interviews, surveys, and focus groups. The data collected determines the amount of time and budget that will be required for the whole process to be completed. This is the stage where you fine-tune your product strategy.
Following are some of the factors that can help you in laying out the scope of the product:
This step comes among one of the most crucial stages of the Product Development Life Cycle Process. Prototyping refers to designing an early draft or sample model of the final product. This phase aims to test the quality, functionality, and usability before starting the actual production process. The phase of prototyping may demand several iterations from you before getting the right one. Prototype sometimes also called MVP (Minimal Viable Product) checks the use or application of the product idea in real life.
Following are some of the areas to pay attention in this stage:
Keeping the prototype of MVP in mind, businesses have to design the initial design of the product. This is the most important phase of the whole process. To bring all the drafts and concepts to life with the maximum results, it should be made sure that all the requirements should be collected and implemented.
The following are the things involved in this stage of development:
This involves developing your product to the final form in which you can release it to your audience. This phase focuses on developing and adding all the necessary components and functionalities of the product. This stage is the result of collective collaboration of technical professionals like engineers, designers, and manufacturers. For software development, the processes included in this stage are writing, testing, and debugging the codes.
On the other hand, developing a hardware product includes things like assembling and testing the physical components in order to create a new product through their collective form. This phase emphasizes factors like usability, performance, and regulatory standards of the product. Before making the product public, it is crucial that you check for any bugs and inaccuracies.
After the product has been developed, making the public aware of your product is crucial to making your own customer range and establishing your name in the market.
Following are the things you will be focusing on in the commercialization stage:
When you make a product public, there is always a need to keep a sharp eye on it. Maintenance of the product includes a number of things from fixing technical bugs to continuously working on enhancements and security. It also includes providing proper support to your customers and keeping everything documented for future use. There will be changes ever since the product goes public, Maintenance ensures that the product remains compatible with all the changes it is going through.
Maintenance makes the product eligible to be integrated with new tools and resources to make it more accessible. Apart from all these factors, maintenance also covers the crucial part of the retirement of the product in its life cycle. Planning what will happen to this product when it will remain viable no more or when a new version of the product is launched.
The journey of your product doesn’t end just on releasing your product. Making sure that you stay updated about what are all the things going on about your product is necessary in order to establish your name in the market along with accomplishing your desired goals and objectives.
Following are some of the measurements that are effective for turning your expectations into your success after the release of your product:
The life of a product you want to launch starts from the moment you think about relatable and effective ideas. These ideas depend on a number of factors like target market, target audience, competitors, and current trends. For curating more effective and long-term products, you should have a team of professionals who can see the future of the market. The process of developing a product includes stages like Ideation, Prototyping, Development, Release, and e-commerce of the product. But the journey doesn’t just end here. You will have to regularly evaluate whether customers are liking it or not. Key metrics like Customer Satisfaction Scores (CSAT), Net Promoter Scores (NPS), and user retention rates are effective when you are measuring the viability of your product.
Continuously reaching out to your customers is another thing that keeps them reminded that they have one additional option when looking for services you offer. With proper execution of all the stages of the Product Development Life Cycle, Customer feedback, and marketing, businesses can surely predict the success of their product.
1 Comment