Do you ever wonder how programs and software are created in such a short amount of time? The development of low-code might be the answer. This innovative approach to creating digital solutions is becoming more and more popular due to its effectiveness and simplicity.
The low code application development methodology was established to adjust to the developing business requirements in software development. It contributes to the transformation of coding from textual to visual by changing and streamlining the development process.
A low code development approach enables the creation of apps and processes with simple logic by anyone with little to no programming experience using drag-and-drop functionality. Low code development is becoming popular among emerging product owners because it allows teams to innovate rapidly without spending a lot of time creating and testing new scripts.
According to Gartner, non-technical people make up about 60% of users of low-code application development tools, and by 2026, their percentage will rise to 80%. Over the last ten years, so-called “low-code” platforms have made it possible for individual developers or even entrepreneurs with a technical background to plan, create, test, and implement those smaller but no less significant apps.
The fact that low-code development is significantly less expensive, helps address the lack of developers, and produces software more quickly to increase time to market are some of its greatest benefits.
The idea of low code application development will be covered in this informative article, along with its features, advantages, difficulties and more. Let’s begin, then!
Teams may build workplace apps and digital solutions using low code, a software development methodology that requires little coding. Low-code development platforms offer authorized scripts, custom code components, and a suite of tools. Then, without the need for intensive code authoring and script testing, users can create new procedures and apps quickly. These systems offer a straightforward drag-and-drop visual development experience. So, without specific coding knowledge, anyone in your company may design and develop business apps.
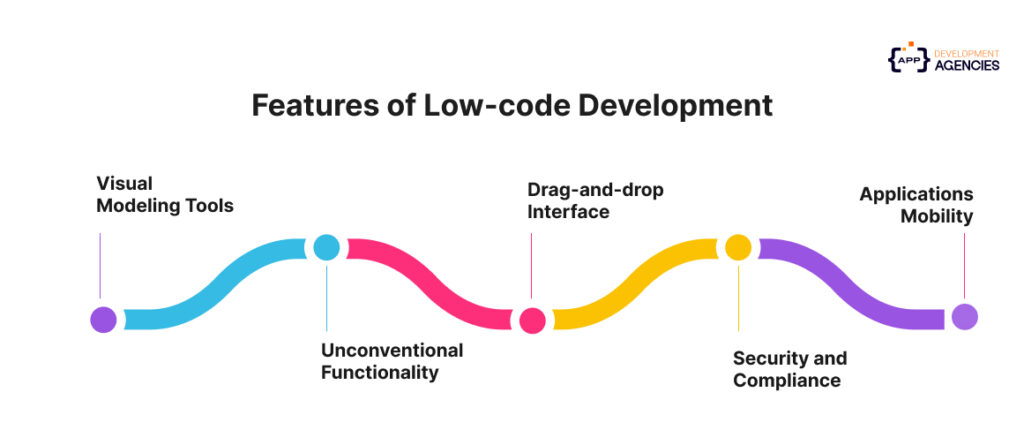
It is crucial to understand the fundamental components of low code before going deeper into its benefits. These essential characteristics provide low-code platforms their strength and flexibility for a range of development requirements:
It takes less time to create apps with visual techniques and templates than it does with code. Built-in modules in low-code systems with visual modeling capabilities allow the intricacies to be reflected in a fashion that is understandable to all users, from advanced developers to non-technical enterprise users.
Leading low-code suppliers offer OOTB (out-of-the-box) capability. This eliminates the need to develop essential application components from the beginning. For instance, some low-code systems offer data storage or app features that interact with customers, including sales process management or service management.
Drag-and-drop enables business users to accelerate their time to market by rapidly developing applications. Code that must be physically written out is greatly reduced by drag-and-drop functionality.
Numerous low-code platforms incorporate compliance rules and security features, like GDPR, that are unconventional for industry standards.
Applications that are accessible and usable on various devices must be developed. Low code technologies enable programs to be deployed on PCs, tablets, and mobile devices without changing the design.
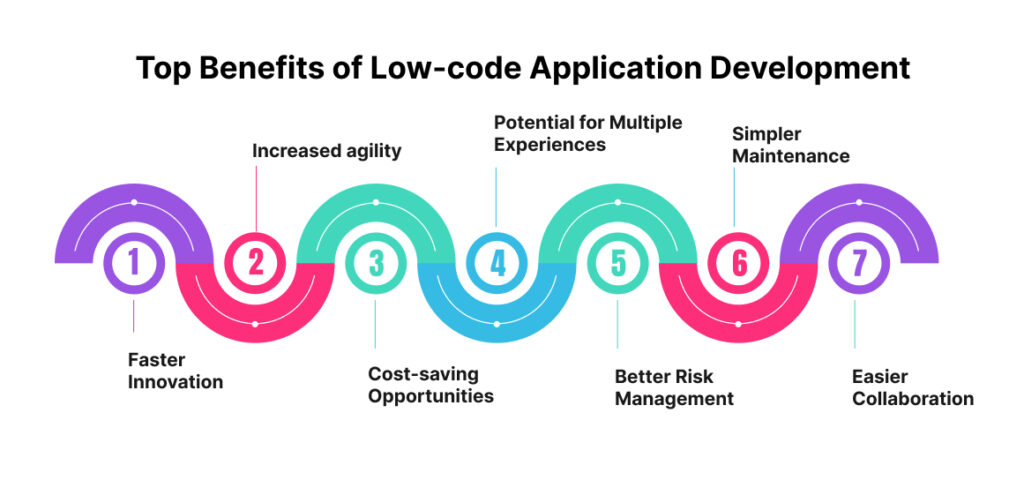
Low-code platforms offer various benefits to organizations, business teams, and developers.
Because low code lets subject-matter specialists lead application development, it can help your company become more creative. Applications can be created by business users, often known as citizen developers having little to no coding skills. Citizen developers improve innovation and product development lifecycles using low-code building blocks to create prototypes and quickly test their new applications. The product development lifecycle can be shortened from months to weeks or even days.
As customer needs grow, businesses must be able to react quickly to the market and create new applications. Low code effectively increases your company’s agility because it allows you to delegate product development to business users and promote application delivery.
You may release your expert developers to work on value-adding projects needing sophisticated coding by implementing a minimal code platform for business users. Additionally, low-code platforms can be integrated with your current data sources and apps. This speeds up time to market and lowers expenses. Implementing low-code application development instead of purchasing commercial off-the-shelf items could also save your money.
Throughout their user journeys, customers can interact with organizations through various digital touchpoints thanks to multi-experience solutions. Low code creates applications for smooth omnichannel experiences on every device by utilizing prepackaged and reusable components.
Security measures that are integrated into low code systems shield your data and apps from unwanted access. Security features can be included from the very beginning of the application development process.
Minimal code techniques make the process of creating apps simpler as compared to traditional coding, requiring manually entering thousands of lines of code. This increases the efficiency of the development process by allowing the business teams to maintain and upgrade products.
Users from all business teams can create apps because of the low code’s simplicity and development speed. Teams can collaborate on several projects and exchange ideas from any location. Additionally, low-code solutions facilitate communication between IT and business teams.
Although “low-code” and “no-code” are sometimes used interchangeably, they’re not synonymous. Both low-code and no-code solutions offer resources for easier app development, so it’s important to consider the distinctions.
The target audience of low-code platforms are professional developers and non-technical business users. They use visual-based modeling to promote the development process and require very little training or expertise. They also let people who know how to code go further, writing code by hand when necessary.
No-code platforms are made especially for business customers and citizen developers, and they don’t require any prior coding knowledge. Although no-code solutions make app creation accessible to almost everyone, they can also result in shadow IT, or the development of unapproved apps inside a company.
Compared to traditional application development techniques, which include teams of skilled software engineers generating large-scale enterprise applications, minimal code has deals even though it might be the greatest option for developing multiple apps. The simplified, highly standardized technique of minimal code may not always be appropriate for the available task. Here are a few things to look out.
Some applications, once written, hardly change, or update only once a year or so. Others may require frequent adjustments, sometimes because of the fluid and delicate nature of the external integrations, and sometimes because the business logic is always changing. Low-code apps might not be as flexible as traditional software, where you can have a dedicated staff of software engineers ensuring everything is operating as it should, even though they are simple to update using visual design tools. Using low code is probably not the best option when maintenance requirements are high.
A visual design tool is used for low-code application development, which are then executed in a standardized runtime environment. Beyond the visual designer, there are several customization options. For instance, Oracle APEX allows you to link to external APIs or add JavaScript code. That is adequate for a lot of things. However, there will be instances in which the interface model of the low-code application just does not satisfy specific needs.
Depending on the app’s complexity, low-code apps are best suited for low- to medium-sized transaction volumes, maybe involving hundreds or even thousands of users at once. That’s more than enough for a lot of company requirements. Low code isn’t the solution for everyone. Consider the software that powers the automated teller system in a bank, or the trading floor of a stock exchange. It takes standard software engineering to achieve that volume and performance. However, because the freight tracker is a low-volume software in and of itself, cheap code can still be utilized for specific activities in those domains, such as generating an executive dashboard.
To what extent does a specific piece of company software need to function properly around the clock? That might not be as important for some apps—like a report writer that is used only once a week—as for a publicly visible app that clients use to check on their sales orders. Although dependable, low-code applications operate in a single runtime environment that could become sluggish or malfunction as a result of an issue with an external data source. Traditionally written and deployed software can be more resilient if that is unacceptable to the business. It can have multiple execution paths if an external service is unavailable, and it can fail over to other copies of the software running on backup servers and even geographically separate data centers in the event of a natural disaster.
Standardized runtime containers, which can be independent environments or containers inside other software, like enterprise databases, are where low-code applications run. In contrast to custom-written cloud-native software, which may be able to run across millions of different servers and cloud data centers, that runtime can manage hundreds or even thousands of contemporary transactions or users.
Additional advantages result from the combination of AI with a low-code platform since it boosts development process creativity and productivity:
Intelligent automation: AI-driven automation technologies can minimize manual labor and improve development by identifying and automating repetitive operations.
Predictive analytics: Developers can anticipate possible problems and enhance app performance by artificial intelligence’s predictive insights.
Improved user experience: More individualized and intuitive apps can be made with AI algorithms to examine user preferences and behavior.
Natural language processing: NLP promotes the development process by improving the platform’s comprehension and interpretation of user needs.
Continuous improvement: As AI learns and adapts, it continuously enhances application functions and development procedures.
Enterprise software can be developed more quickly and effectively with low code. As we’ve seen, not all tasks require a low-code method; in certain cases, a traditional software engineering technique is necessary due to the technological needs of a given project. On the other hand, employing low code can significantly reduce the amount of work required to app development, reducing the time needed from months to days and using fewer personnel and resources.
Modern low-code platforms have many advantages, including a very user-friendly developer experience and tools that can increase productivity and reduce faults as compared to older low-code systems. Furthermore, low code can reduce the backlog of software development at your company, enabling you to handle issues and take advantage of possibilities more rapidly due to its easier maintenance and reduced development expenses. It deserves a closer look.